Guide to Rectifying Memory Issues on PCs

Guide to Rectifying Memory Issues on PCs
Using the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool, you can diagnose memory issues on your Windows computer. If there is a problem, it will return an error. One common Windows Memory Diagnostic error you may encounter is “Hardware problems were detected; contact manufacturer,” followed by the “You have a memory problem” dialog.
This error can be a false positive. You can also confirm the same by using a third-party memory diagnostic tool. In case of a hardware issue, you may need to replace the memory stick or repair the memory slot, if possible.
What Causes the Windows Memory Diagnostic Hardware Problems Were Detected Error?
This error is often triggered after a blue screen of death (BSOD) or the system freezing issues. The reason for the error can vary and include faulty memory slots and memory sticks. It can also be a false positive due to a Windows OS glitch.
1. Check for Overclocking Issues
Incorrect overclocking can cause hardware issues. While faster RAM can help you achieve good performance, it is important to consider the hardware limitations before applying the tweaks.
If you have overclocked your RAM, try to lower the frequencies to see if the error goes away. Do this until you find a safe frequency, or reset it to factory default settings.
If you are unsure about the default memory frequencies, try to perform a BIOS reset. Load the BIOS default, which should reset the RAM frequencies to its factory default. Refer to your motherboard manufacturer manual for specific instructions.
2. Run the Hardware Troubleshooter
The built-in Windows hardware troubleshooter can scan for hardware-related issues and even try to perform a repair if possible. If you haven’t tried already, run the hardware troubleshooter using the Command Prompt to resolve the problem.
Note that it is a legacy troubleshooter, and you may not find it in the Windows 11 version newer than 22H2.
To run the Windows Hardware Troubleshooter:
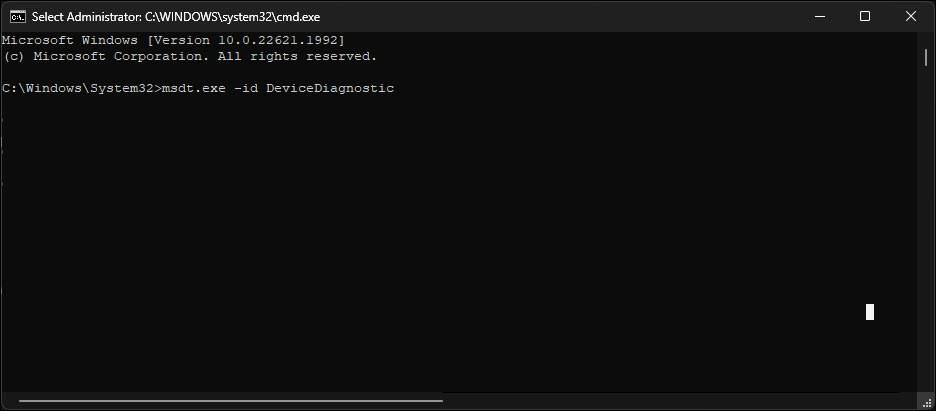
- Press the Win key and type cmd.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as administrator. Click Yes if prompted by the User Account Control dialog.

- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and press Enter:
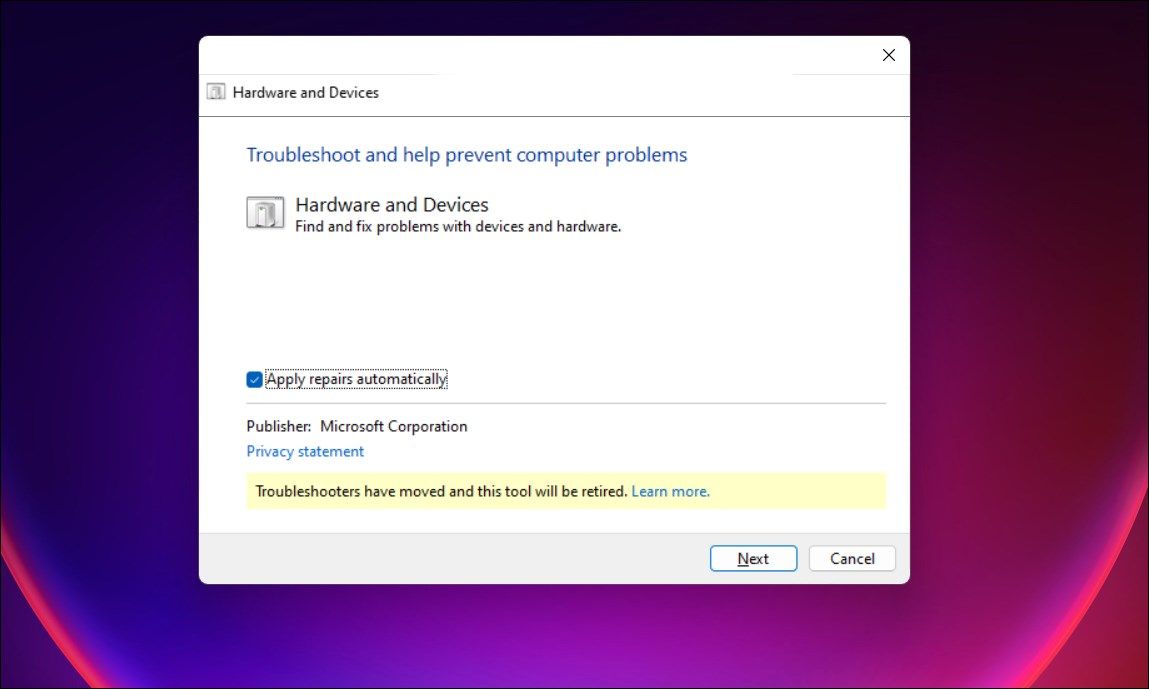
msdt.exe -id DeviceDiagnostic - In the Hardware and Devices dialog, click Next. By default, the troubleshooter is set to apply any repairs available. To disable automatic repair, click Advanced and uncheck the Apply repairs automatically option.

- It will scan your computer for issues, which may take a few minutes. If an issue is detected, select to automatically apply the repair.
- If the suggested problem is unrelated to memory, you can skip it to see the next problem. The troubleshooter will detect additional issues. If an issue is found, apply the fixes and check for any improvements.
3. Remove and Reinsert Your Memory Sticks
If you work with multiple memory sticks, remove all the sticks and wipe the card to remove dust and debris. Reboot the computer and check for any improvements.
Still not working? Remove all but one stick and reboot your computer to see if the error is resolved. If not, repeat the procedure with all the sticks individually to determine and detect a faulty memory stick. If you find a faulty memory module, you can get a replacement or claim a warranty if available.
If the issue persists, check your memory (RAM) slots for fault. Insert a memory stick into one of the slots and reboot your computer. If there is no error, test other slots and check if you can find a malfunctioning slot.
If you determine a faulty RAM slot to have caused the issue, repairing it is tedious. First, RAM slots aren’t easily accessible like memory sticks. Second, to replace the slot, you’ll need to find a spare but compatible motherboard with working slots and then solder the connections onto your motherboard.
If repairing the slots is not possible, your only option is a motherboard replacement. Depending on your system configuration, this can be an expensive solution. Or you can continue to use the system without utilizing the faulty memory slot, albeit with reduced performance.
4. Test Your RAM with MemTest86+
If the troubleshooter fails to detect any issue, you can perform a memory test using the MemTest86+ utility. It is an open-source memory testing tool to check for fails in your computer memory.
MemTest86+ is a bootable utility and cannot be used from within Windows. To test your RAM with Memetst86+, you’ll need a USB drive. You can use the Memtest86+ Windows installer to create a bootable drive and boot from it.
As of writing this article, Memtest86+ wasn’t compatible with Windows Secure Boot. So, you’ll need to disable Secure Boot to use the utility.
To perform a memory test using Memtest86+:
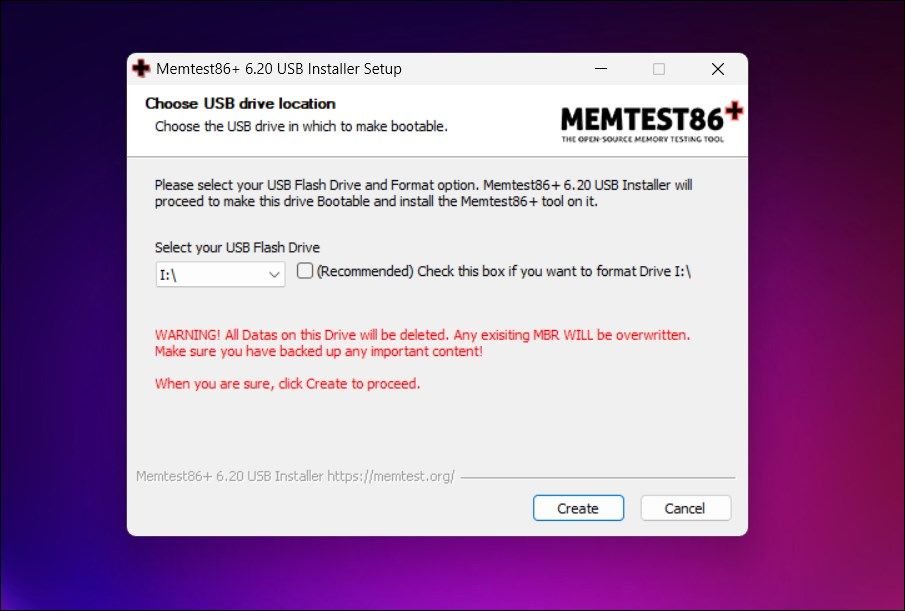
- Connect a USB flash drive to your computer. Take a backup of important data in the drive, as all the data will be deleted during the process.
- Next, go to the metest86+ page and download the latest version available.
- Run the installer and select your USB drive. Make sure to select the format option.

- Click Next and wait for the installer to create a bootable drive.
- Next, if you haven’t already, disable Secure Boot on your Windows computer .
- Next, power off your computer. You may also need to clear your motherboard CMOS to reset your BIOS to factory default settings. You can also reset BIOS to its default configuration from the BIOS menu.

- Next, plug the Memtest86+ bootable USB drive into your computer and turn it on.
- Boot into the Boot Menu and select the bootable USB drive as the boot device. The hotkey key to enter the Boot Menu may vary depending on your computer manufacturer. You can press F9 on an HP computer, F12 on a Dell computer and so on to access the Boot Menu.
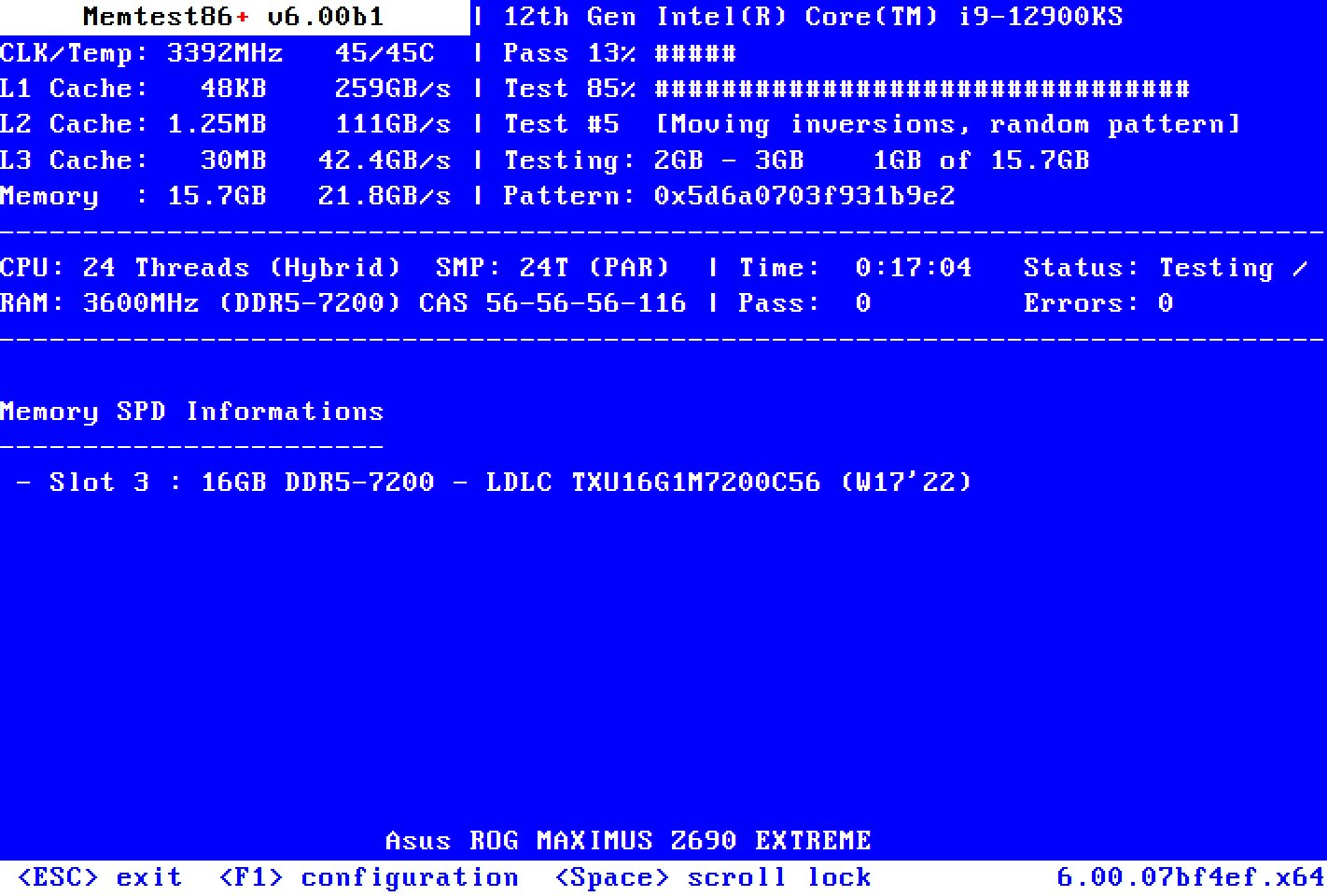
- Memtest86+ will automatically start the memory integrity check. Let Memtest86+ complete at least 2 passes; the more, the better. Press the Esc key to stop the test if there are no errors after multiple passes.
If an error is detected during testing, it is likely a case of faulty RAM and may need replacement. But to be on the safer side, ensure you test each RAM separately to find the odd one out.
Not all the errors detected by the Memtest86+ are due to faulty hardware. Some errors may occur due to compatibility issues. Check your RAM module and the motherboard specifications to determine any compatibility issues. You can also test the RAM modules by inserting them into a different motherboard and see if it works.
5. Perform a Repair Reinstall or Clean Install Windows
If the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool continues to show the hardware problem was detected error, even after the Memtest86+ passed the test, check if the problem is due to issues with the Windows operating system.
To fix critical issues with your Windows image, you can perform a repair reinstall of Windows 11 without deleting apps . If that does not work, perform a clean install. This will reinstall the operating system but delete all your apps and data from the computer. So, backup any data you need before attempting a clean install.
Fixing the Memory Diagnostic Tool “Hardware Problem Detected” Error
When an error is detected with your memory modules, the Windows Memory Diagnostic tool will show an error. While memory-related issues are often due to faulty hardware, make sure to run the device hardware troubleshooter to detect and resolve minor glitches.
Alternatively, perform a memory integrity check using the Memtest86 tool. If the memory modules pass the Memtest86, you may need to perform a Windows OS clean install to fix issues with the Windows system files.
This error can be a false positive. You can also confirm the same by using a third-party memory diagnostic tool. In case of a hardware issue, you may need to replace the memory stick or repair the memory slot, if possible.
Also read:
- [New] 2024 Approved Efficiency at Play Reducing YouTube Video Length
- [New] 2024 Approved Top 5 Budget-Friendly Gaming Mice (Under $100)
- In 2024, Looking For A Location Changer On Xiaomi Redmi Note 12 Pro 5G? Look No Further | Dr.fone
- Integrating Images Into Your Insta World
- Key Steps Unveiled: Navigating Disks in W10 & W11 Systems
- Mindfulness Meets the Mind: Cognitive & Emotional Responses to Meditation
- Power Up Your VMs in Windows Using These Top 6 Enhancers
- Tackle Non-Selectable Text in Windows-Based PDF Documents Easily
- The Complete Tutorial to Launch W11's Administrator PowerShell
- Top 3 Highly-Rated Text to Speech Browser Addons for Chrome Users
- Top 8 Economical Video Call Applications Cross-System Compatibility
- Tripod Alignment Secrets for Clearer Videos for 2024
- Why Choosing Windows 11 Is a Wise Decision over MacOS
- Title: Guide to Rectifying Memory Issues on PCs
- Author: Joseph
- Created at : 2025-02-03 23:27:27
- Updated at : 2025-02-11 06:48:28
- Link: https://windows11.techidaily.com/guide-to-rectifying-memory-issues-on-pcs/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.