
Fast Startup Mastery in Windows 11 - A Comprehensible Guide

Fast Startup Mastery in Windows 11 - A Comprehensible Guide
Windows 11 has kept many of the useful features from its predecessor, including Fast Startup. As the name suggests, Fast Startup allows your computer to start up faster after a shutdown.
Hibernate-capable Windows 11 systems come with Fast Startup enabled by default. If you want to turn on or off Fast Startup in Windows 11 manually, this guide will show you how.
Why Should You Enable or Disable Fast Startup?
With the release of Windows 8, Microsoft updated and renamed the default shutdown scenario as Fast Startup. It begins with the shutdown process by writing data to disk, similar to the hibernate process.
However, unlike hibernation, it logs off all the user sessions and writes the remaining boot information to the hiberfil file. So, instead of loading everything from scratch, Windows loads data from the Hiberfil.sys file into memory when you restart your computer, significantly reducing the boot time.
That said, Fast Startup is not without its shortcomings. For example, according to Microsoft , you may face difficulties installing Windows updates on Fast Startup-enabled systems. Another reason is the missing dual boot option because of the disabled delayed start function . To learn more, read our explainer on how Fast Startup works and why you should disable it .
How to Check if Fast Startup Is On or Off
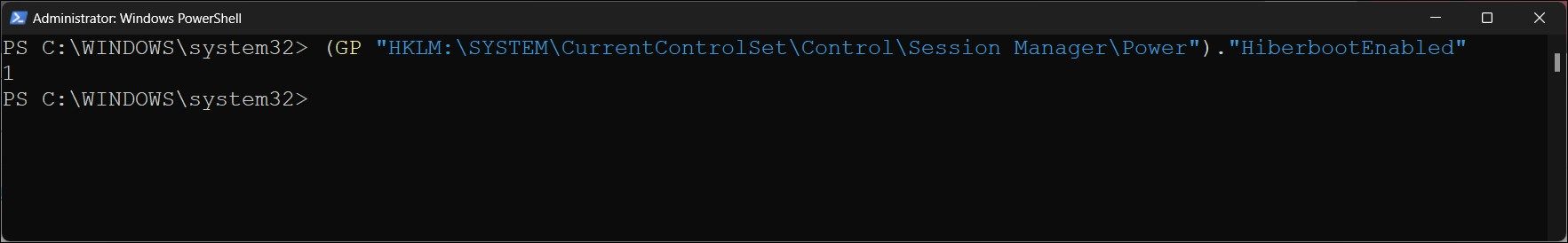
Often, a major Windows feature update may overwrite the power settings and disable Hibernate, thus disabling Fast Startup. Or you may experience unusual boot behavior even when you think Fast Startup is on. Before attempting to troubleshoot your computer, check if Fast Startup is on or off.
You can use Command Prompt to check the Fast Startup status:
- Press the Win key and type powershell.
- Right-click on PowerShell and select Run as administrator. Click Yes if prompted by User Account Control.
- In the PowerShell console, copy and paste the following command and press Enter:
(GP "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Power")."HiberbootEnabled" - The above command uses the Get-Item (GP) cmdlet to retrieve power-related settings and information about the HiberBootEnabled value in the Windows Registry.
- A returned value of 1 means Fast Startup is On. A 0 would indicate Fast Startup as Off.
If the hybrid boot is off, you can follow the steps below to enable Hibernation and then Fast Startup on your computer.
To turn on Fast Startup, you must have Hibernate feature enabled on your computer. To check if Hibernate is enabled on your PC:
- Press the Win key to open the Start menu.
- Next, click on Power (power icon) and check if Hibernate is shown among other power options.
- If disabled, the Hibernate option will not appear in the Power menu.
Alternatively, check if Hibernate, while available, is hidden in the Control Panel. To do this:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type powercfg.cpl and click OK to open Power Options in Control Panel.

- In the Control Panel dialog, click Choose what the power buttons do in the left pane.
- Click Change settings that are currently unavailable.

- Under Shutdown settings, check if Hibernate is available. If available, select Hibernate and click Save changes to show Hibernate in the Power menu.
If the Hibernate option is missing, you can enable it using a Command Prompt command.
How to Enable Hibernation in Windows 11
Fast Startup is only available on systems compatible with the Hibernate feature available on almost all modern computers. However, this option is often disabled by default on lower-end systems.
To enable Hibernate on Windows 11:
- Type cmd in the Windows search bar.
- Right-click on Command Prompt and select Run as Administrator.
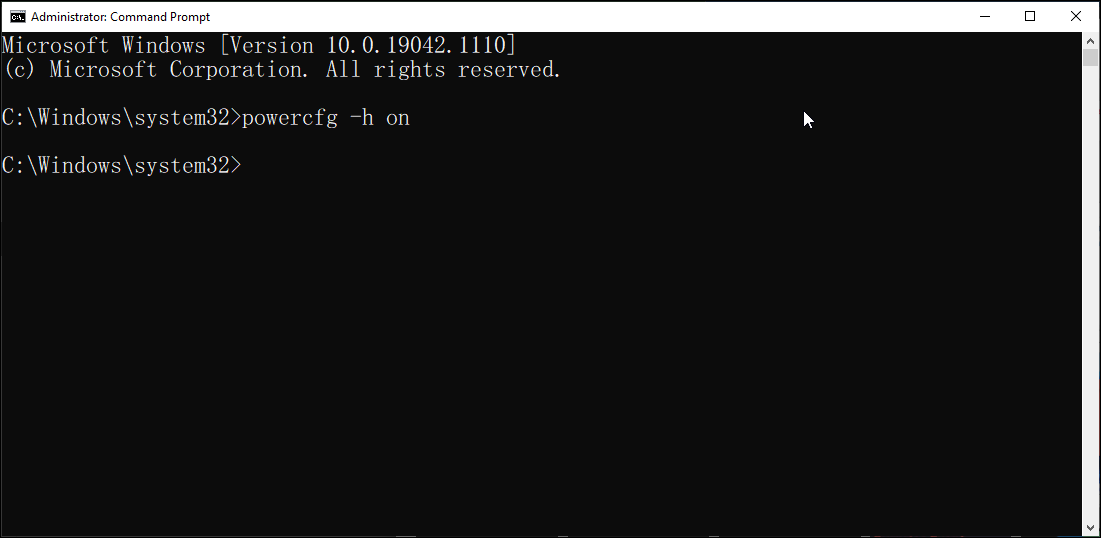
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and hit enter to turn on Hibernate:
Powercfg -h on
Now that you have enabled the hibernate feature, below are the various ways to enable and disable Fast Startup on your Windows computer.
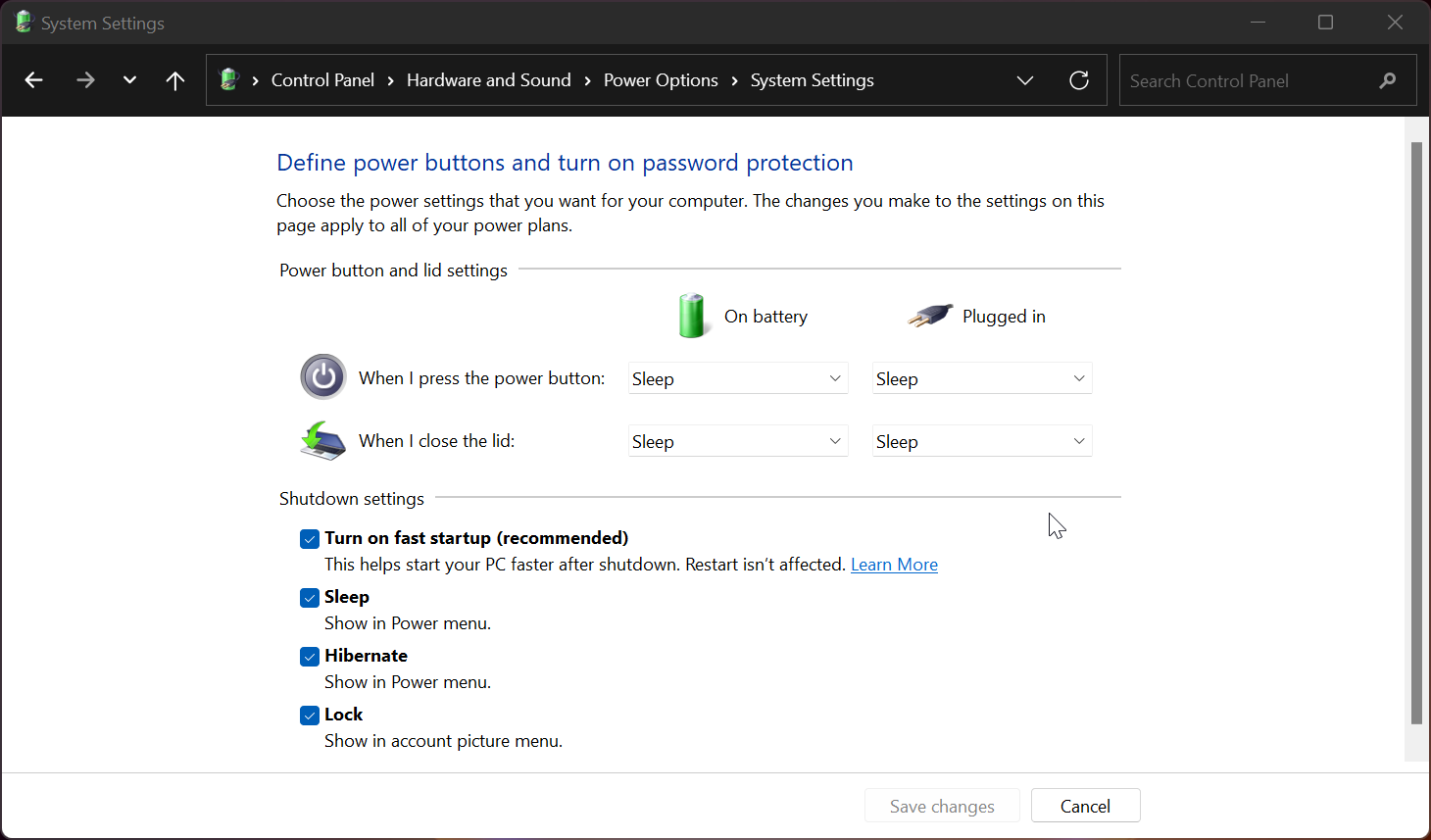
The easiest way to turn on Fast Startup is via the Control Panel’s power settings. Here’s how to do it.
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type control and click OK to open the Control Panel.
- Go to System and Security and then click on Power Options.
- In the left pane, click on Choose what the power buttons do.
- Next, click the Change settings that are currently unavailable link.
- Under the Shutdown settings section, check the Turn on fast startup (recommended) option to turn on the feature.
- Uncheck the Turn on fast startup option to disable Fast Startup.
- Click Save changes to apply the changes.
How to Turn On or Off Fast Startup Using the Registry Editor
The next set of methods involves modifying the Windows registry. If something goes wrong, restoring your system to a functioning state can become difficult. So, create a restore point before attempting to edit your registry entries. This will allow you to undo the changes if your system breaks during the process.
Once done, do the following:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type regedit and click OK. Click Yes when prompted by UAC.
- In the Registry Editor, navigate to the following location:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Power - You can also copy/paste the above path for quicker navigation.
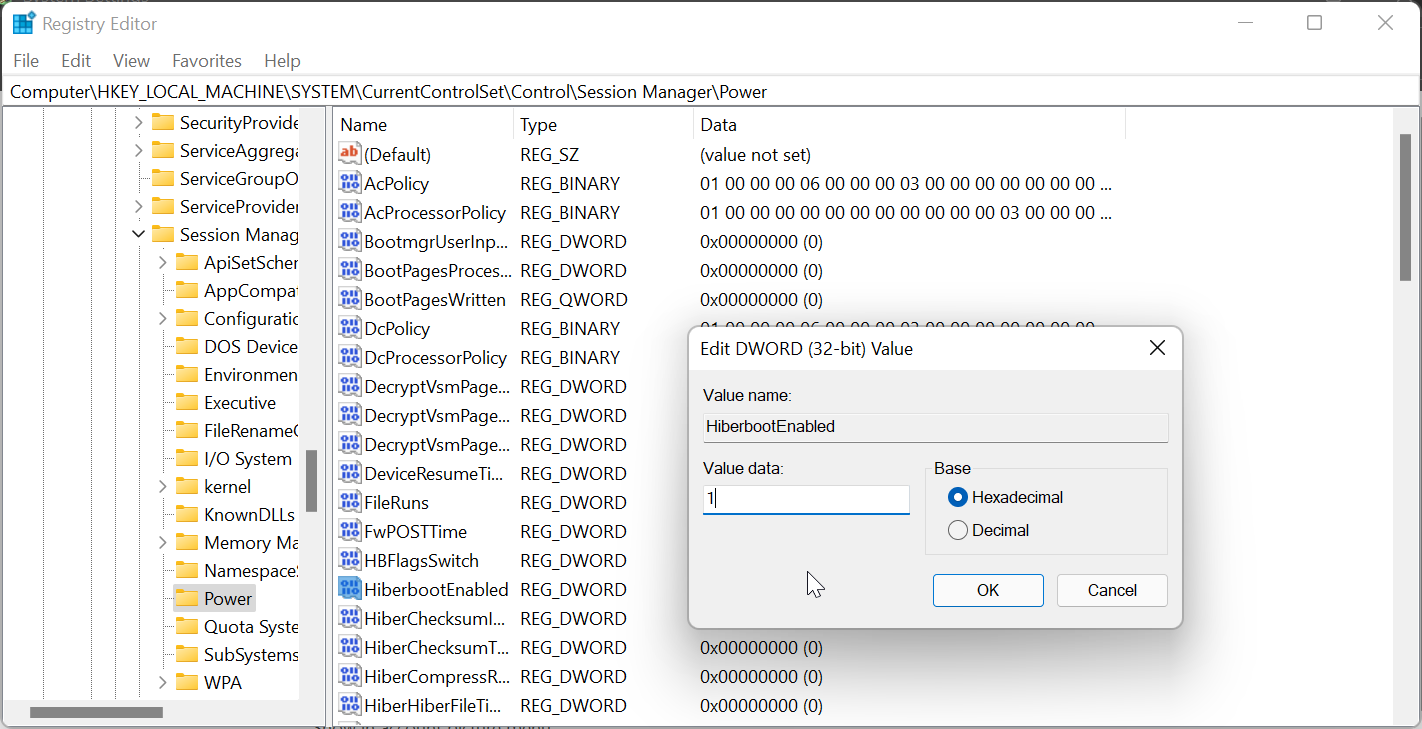
- In the right-pane, scroll down and locate the DWORD value HiberbootEnabled.
- Right-click on HiberbootEnabled and select Modify.
- Type 1 in the Value data field and click OK to save the changes.
- To turn off Fast Startup, enter 0 in the Value data field and click OK.
- Close the Registry Editor and reboot your computer.
How to Turn On or Off Fast Startup Using a Registry File
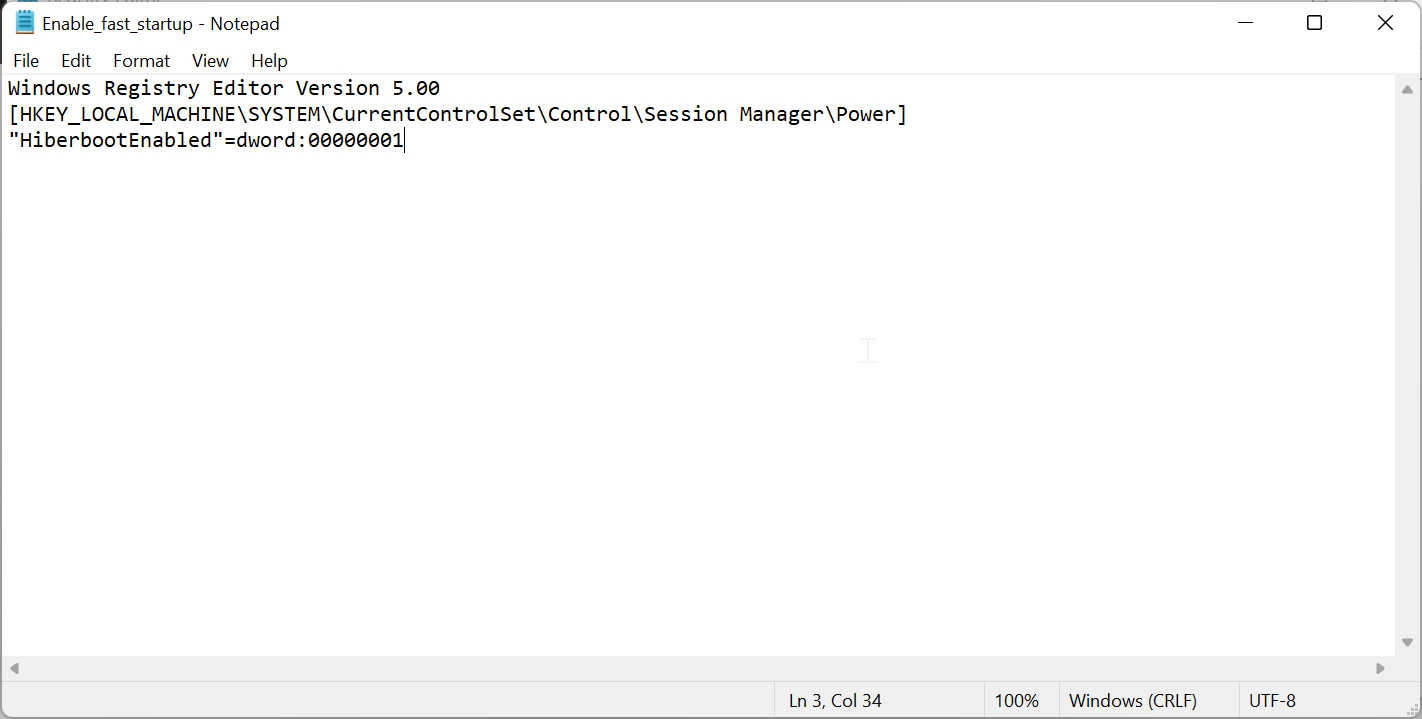
If you don’t want to work with the Registry Editor, you can create a REG file and run it to achieve the same. Here’s how to do it.
- Press the Win key, search for the Notepad app and open it.
- To enable Fast Startup, copy and paste the following code in the Notepad file:
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Power] "HiberbootEnabled"=dword:00000001 - To disable fast startup, copy and paste the following code instead.
Windows Registry Editor Version 5.00 [HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Session Manager\Power] "HiberbootEnabled"=dword:00000000 - Click on File and select Save As.
- Enter file name as Enable_fast_startup.reg or Disable_fast-startup.reg.
- Click on Save as type drop-down and select All Files.
- Next, click Save.
- Double-click on the Enable_fast-startup.reg file to run. Then click Yes, and Yes to confirm the action.
How to Enable or Disable Fast Startup in the Group Policy Editor
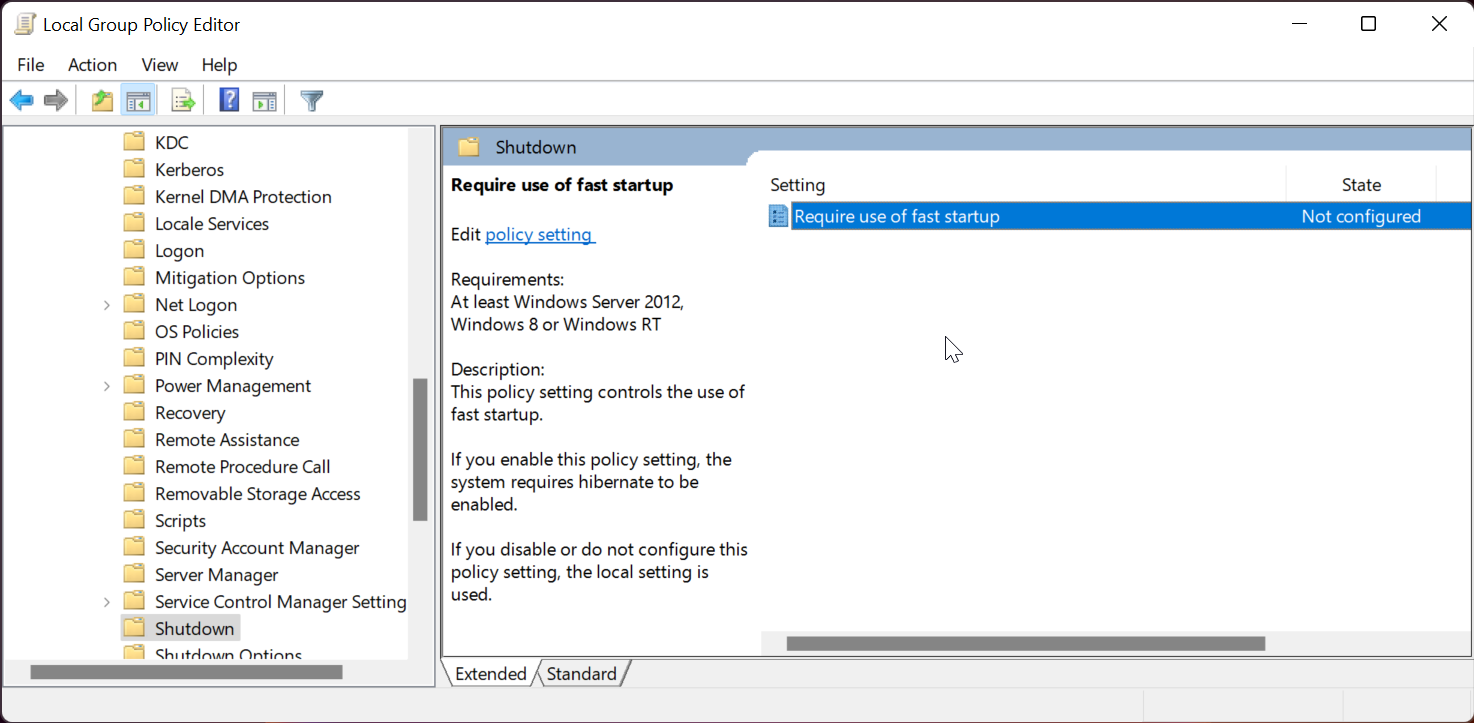
Group Policy Editor allows you to configure your Group Policy settings to allow or restrict features as required. You can use it to enable or disable the Fast Startup feature on your Windows computer.
Note that the Group Policy Editor is only available in Windows Edu, Pro, and Enterprise editions of the OS. If you are running Home, here’s how to access the Group Policy Editor in Windows Home .
Follow these steps to turn on Fast Startup on Windows 11:
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type gpedit.msc and click OK to open Group Policy Editor.
- In Group Policy Editor, navigate to the following location:
Computer Configuration\Administrative Templates\System\Shutdown - In the right pane, right-click on Require use of fast startup and select Edit.
- Select Enabled to turn on Fast Startup.
- Or Select Disabled to turn off Fast Startup.
- Click Apply and OK to save the changes.
How to Turn Off Fast Startup Using the Command Prompt
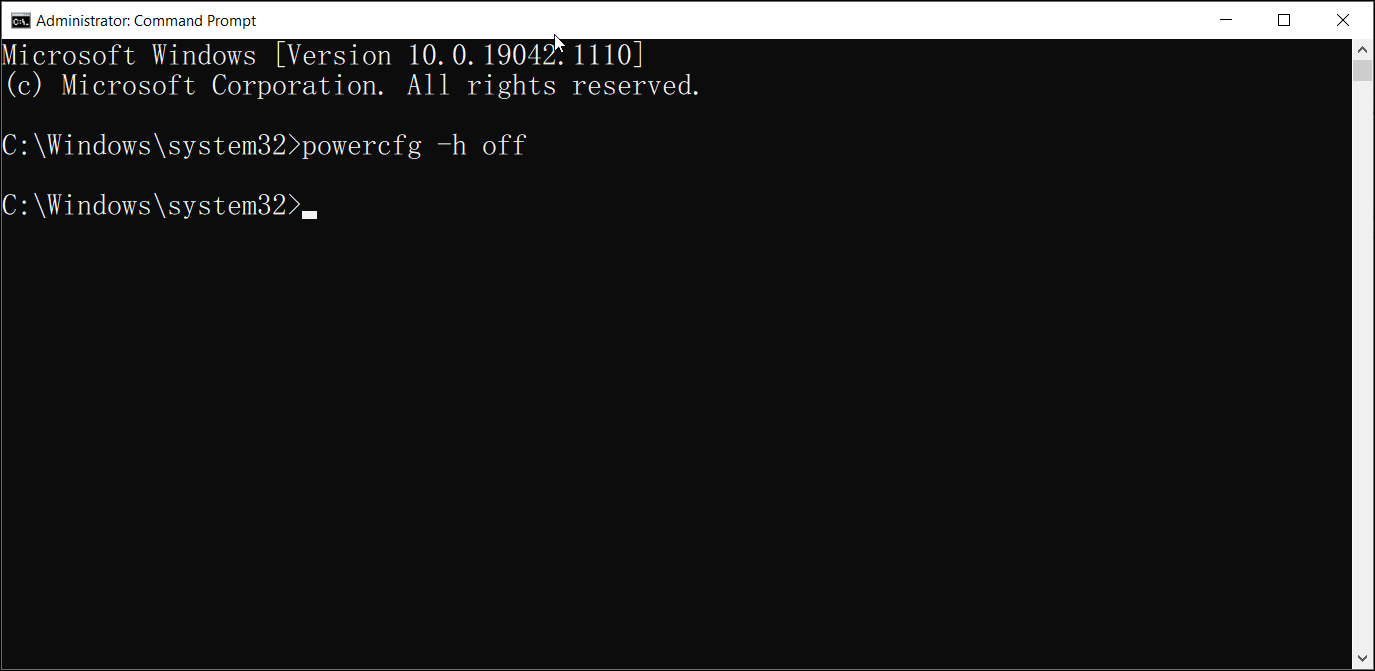
Since fast startup depends on the Hibernate feature, you can disable Hibernate to turn off Fast start. However, this will also turn off Hibernate in Power options, so tread carefully.
- Press Win + R to open Run.
- Type cmd into the box and then press Ctrl + Shift + Enter to open the Command Prompt as administrator.
- In the Command Prompt window, type the following command and hit enter:
Powercfg -h off - This will disable the Hibernate feature and also turn off Fast Startup.
Making Your Windows 11 PC Boot Better
The Fast Startup feature works like a charm on the older and slower systems with traditional HDDs or hybrid configurations. While you can shave off a few seconds even on an SSD, the incompatibility with dual boot and issues with Windows updates is an annoyance for many.
Whether you want to turn Fast Startup on or off depends on what problem you are trying to solve. Try experimenting with the feature to see if it works for you. If not, you can always undo the changes.
Hibernate-capable Windows 11 systems come with Fast Startup enabled by default. If you want to turn on or off Fast Startup in Windows 11 manually, this guide will show you how.
- Title: Fast Startup Mastery in Windows 11 - A Comprehensible Guide
- Author: Joseph
- Created at : 2024-08-15 16:07:09
- Updated at : 2024-08-16 16:07:09
- Link: https://windows11.techidaily.com/fast-startup-mastery-in-windows-11-a-comprehensible-guide/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.

 Forex Robotron Basic Package
Forex Robotron Basic Package