Deciphering Drives: C: Vs D: Explanation

Deciphering Drives: C: Vs D: Explanation
You’ll most likely find a C: and D: drive when you visit File Explorer on a Windows computer. Ever wondered about the difference between a D: drive and a C: drive and which one you should use? You’re in the right place!
Let’s compare both drives to see if their differences change your storage preferences.
What Is the Local Drive C?
First, a local disk or local drive is a hardware storage device installed directly within your computer to enable you to store and retrieve data easily. Unlike external storage devices that you have to mount to access data, or cloud storage that requires an internet connection, local drives live inside your computer.
Computers come with a local disk (more commonly known as a hard disk drive or solid-state drive ) installed. If the pre-installed hard drive size is insufficient, you can purchase other storage devices, like USB drives, CD-ROMs, and memory cards to use with your computer.

Now, your Windows computer assigns alphabets to enable you to access these drives. It’ll also assign alphabets to partitions—defined areas with a determined size on a drive. For example, if your computer has a 500GB hard disk drive (HDD) or solid-state drive (SSD), you might have two partitions with 250GB each.
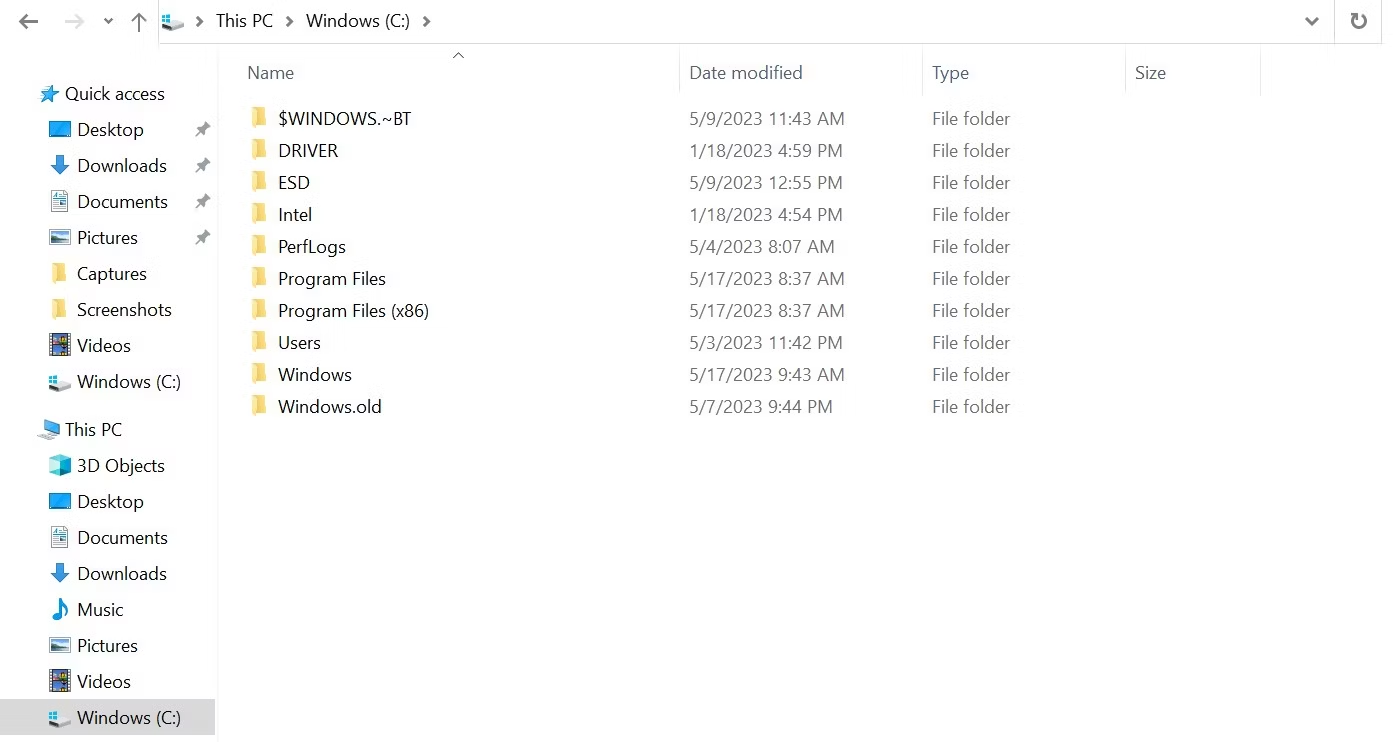
The C: drive is your Windows computer’s primary drive or partition. This drive or partition is assigned the first available letter, as Windows starts naming drives from the letter C instead of A or B .
Manufacturers install the operating system and other relevant software on the C: drive. If your computer has a 1TB HDD or SSD with two 500GB partitions, the C: drive is the hard disk partition that serves the above function. Alternatively, if your computer has a 250GB hard drive with one partition, then it’ll be your drive (C:).
The C drive is typically denoted as (C:), Windows (C:), or Local Disk (C:). You can access your local disk C: by clicking My Computer (on older Windows versions) or This PC (on newer Windows versions) in File Explorer. To open File Explorer on your computer, press the Windows key + E.
Characteristics of the C: Drive
This is your Windows computer’s primary drive or partition. Here are the features of the C: drive:
- The C: drive provides storage space for your operating system and system files. This local drive is integral, enabling your computer to boot and function.
- Typically, the C: drive houses all the applications (with their file data) you or the manufacturer installs, including other related system files. All your computer’s software and files are on the C: drive. Therefore, most programs and software are installed into the local disk C: by default.

- While it is possible to use the D: drive or C: drive for games and other non-essential apps, some app components must be installed on your primary drive to function properly, as it houses your OS.
- If the drive C: is an SSD, it’ll likely be faster than an external HDD assigned the letter D. However, a heavily fragmented drive C: with numerous read and write operations may be slower than a D: drive with fewer operations. But this will vary greatly based on each computer’s specifications.
- Although the primary partition or drive is automatically assigned letter C, you can swap drive letter C for another letter , as it’s not set in stone. However, it’s typically not worth the hassle!
Remember that the letter C in itself doesn’t mean anything. However, it’s typically assigned as an identifier for the local drive containing your Windows OS.
What Is the Local Drive D?

Image Credit: DAMRONG RATTANAPONG/Shutterstock
The D: drive is a secondary drive or partition following the C: drive. Remember, the drive C: is automatically assigned the letter C because it is the primary partition or drive housing your Windows operating system (OS).
D: is the next drive you add to your computer after the drive (C:). So if you have a 500GB HDD or SSD with two 250GB partitions and the first partition has been assigned the letter C, the second partition will automatically be assigned the letter D.
Similarly, if you have a 250GB hard drive with one partition already assigned the letter C and a CD or DVD player, your D: drive will most likely be a CD or DVD drive.
Otherwise, your D: drive can be a removable flash drive or memory card—any additional local drive you connect to your computer after the drive (C:). Once the letter D is taken, your Windows computer will assign the letter E (up to Z) to any other local disk you attach to your device.
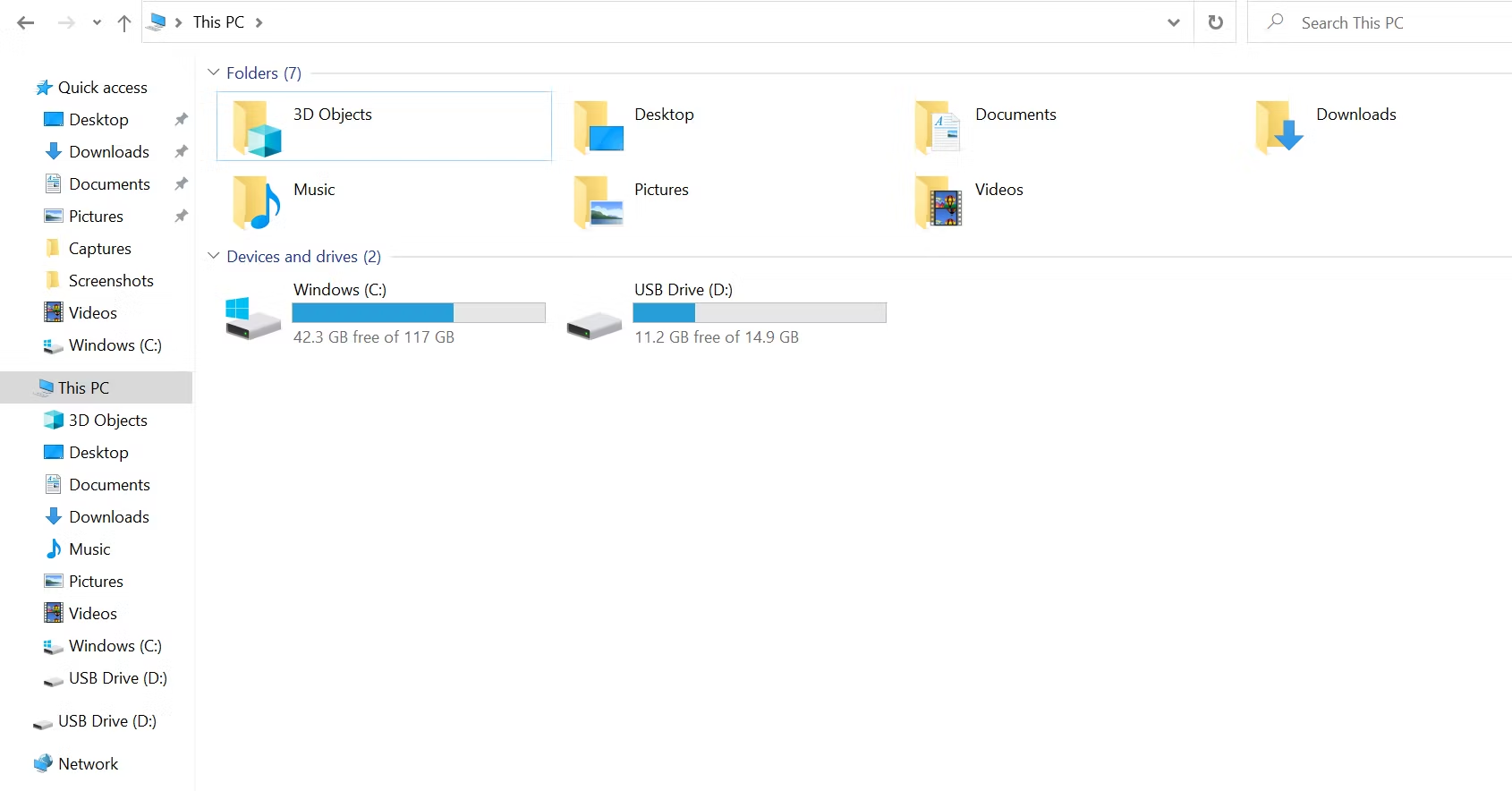
Characteristics of the D: Drive
Drive D: is a secondary local drive attached to your system after the primary drive with your OS. Here are the common features of the D: drive:
- Drive D: is typically the next storage device connected to your computer after the C: drive. Some people use it as a backup or recovery device, while others use it to store personal files like photos, videos, audio files, documents, and APKs. If drive C: crashes, your data in drive D: will remain safe.
- You can also use this drive to store large apps, like games, that need additional storage space and aren’t vital to your device’s operation.
- Depending on your computer’s makeup, the drive D: could be a partition of an internal hard drive, a secondary internal hard drive, an internal disc drive (CD, DVD, or Blu-ray), or an external flash drive.

- Unlike Drive C: you can easily change the alphabet assigned to this secondary drive—with fewer consequences. But, there’s hardly any need to.
Similar to the C: drive, the “D” here isn’t indicative of anything on its own. However, the letter D is usually assigned to any storage device that’s installed after the drive containing your Windows OS.
What About macOS and Linux Computers?
You’ll only find the C: and D: drive on a Windows computer. While Windows assigns letters from C to storage devices to access them easily, Linux and macOS don’t use letters. Instead, they use a unified system hierarchy, placing all files under a root directory.
Drives containing a Linux or macOS operating system are mounted at / (the system root) instead of C: as in Windows computers. Other drives and storage devices can be mounted in arbitrary folders. For instance, external storage devices on Linux computers are typically accessed at /mount instead of a D: drive or E: drive.
C: Drive vs. D: Drive: Which Should You Use?
The C drive is the local disk from which your operating system runs. It houses all your computer’s default programs, applications, and system files. Meanwhile, the D drive is a secondary hard drive on which you can store data that isn’t vital for your computer’s operations.
You may decide to leave only your Windows files on the C: drive and store personal files and non-essential apps on your D drive. However, whichever drive you choose, note that the letter isn’t indicative of performance, speed, or capability. C, D, or E-Z, are identifiers that can refer to a variety of storage devices.
Let’s compare both drives to see if their differences change your storage preferences.
Also read:
- [Updated] In 2024, Leading Makers Premium Instagram Highlight Craftsmen
- [Updated] Win10's Best Screen Capture and Recording Options for 2024
- 2024 Approved Digital Artisans' Exclusive Summit
- Detailed Evaluation of the Latest SnappyDriver Install Version (1.13) for Windows Users
- Exposing Limits: The CPU Performance Spectrum
- Fixing D3DX9_39 Error: Steps to Recover DLL
- Foldable Future Arrives? Intriguing Forecast for iPhone's New Form with Tentative Price, Release Info & Speculations Shared
- Guidelines to Selectively Turn Off Windows 11 Services
- How to Fix ALT Codes Not Working on Windows
- In 2024, Tips for Making Facebook Ad Videos Memorable
- Mastering Acoustic Transitions in Audacity Pro Suite for 2024
- New 2024 Approved Unleash Pro-Level Video Editing with 64-Bit Software
- Quicken Pace: Elevating Gameplay with Better Frames
- Reviving Windows Services Command Prompt Tool: A List of 7 Remedies
- Stop Mouse Accel: Tips for Win 11 Users
- Top Free Software Para Crear Una Copia De Seguridad De Su M.2 SSD
- Windows 11 Woes: Alternatives Without Upgrading
- Title: Deciphering Drives: C: Vs D: Explanation
- Author: Joseph
- Created at : 2025-01-13 04:27:30
- Updated at : 2025-01-16 09:35:18
- Link: https://windows11.techidaily.com/deciphering-drives-c-vs-d-explanation/
- License: This work is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 4.0.